 Regardless of the industry, when starting a new business, project, brand, or venture, the first step is to determine the proper legal structure. This typically becomes a choice between a corporation or a limited liability company.
Regardless of the industry, when starting a new business, project, brand, or venture, the first step is to determine the proper legal structure. This typically becomes a choice between a corporation or a limited liability company.
The purpose of this post is to give you a broad strokes overview of a few legal structures so you can have an informed discussion with your attorney, accountant, or other professional advisor.
My goal is to explain the most important points for each in less than a three minute!
__________________________________________________________________________
Below I have 3 items for you that quickly give you a rundown on the most important points.
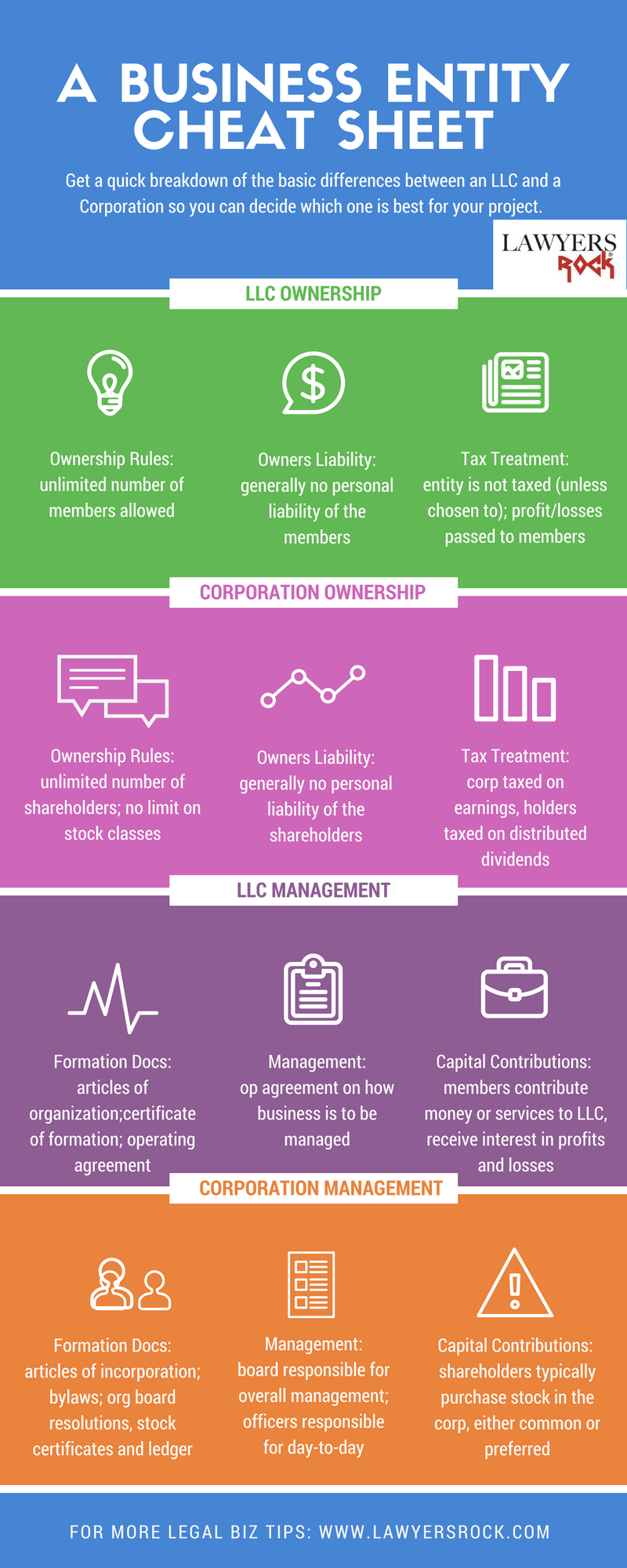
- A Infograph that shows the difference between LLC and Corporations.
- A video on why you should form an entity.
- A table breaking down the differences between LLC and Corporations.
__________________________________________________________________________
Infograph: Differences Between an LLC or a Corporation?
Want to share this image on your site? Just copy and paste the embed code below:
_____________________________________________
Video on Why You Should Form an LLC or Corporation
__________________________________________________________________________
Table on Differences Between LLC and Corporation
LLC Explained – Corporation Explained
Different Forms of Business Entities
|

No comment yet, add your voice below!